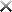本当質問と回答の練習モード
現代技術のおかげで、オンラインで学ぶことで人々はより広い範囲の知識(S90.20有効な練習問題集)を知られるように、人々は電子機器の利便性に慣れてきました。このため、私たちはあなたの記憶能力を効果的かつ適切に高めるという目標をどのように達成するかに焦点を当てます。したがって、SOA Certification S90.20練習問題と答えが最も効果的です。あなたはこのSOA Security Lab有用な試験参考書でコア知識を覚えていて、練習中にSOA Security Lab試験の内容も熟知されます。これは時間を節約し、効率的です。
信頼できるアフターサービス
私たちのS90.20試験学習資料で試験準備は簡単ですが、使用中に問題が発生する可能性があります。S90.20 pdf版問題集に関する問題がある場合は、私たちに電子メールを送って、私たちの助けを求めることができます。たあなたが新旧の顧客であっても、私たちはできるだけ早くお客様のお手伝いをさせて頂きます。候補者がSOA Security Lab試験に合格する手助けをしている私たちのコミットメントは、当業界において大きな名声を獲得しています。一週24時間のサービスは弊社の態度を示しています。私たちは候補者の利益を考慮し、我々のS90.20有用テスト参考書はあなたのS90.20試験合格に最良の方法であることを保証します。
要するに、プロのS90.20試験認定はあなた自身を計る最も効率的な方法であり、企業は教育の背景だけでなく、あなたの職業スキルによって従業員を採用することを指摘すると思います。世界中の技術革新によって、あなたをより強くする重要な方法はSOA Security Lab試験認定を受けることです。だから、私たちの信頼できる高品質のSOA Certification有効練習問題集を選ぶと、S90.20試験に合格し、より明るい未来を受け入れるのを助けます。
S90.20試験学習資料の三つバージョンの便利性
私たちの候補者はほとんどがオフィスワーカーです。あなたはSOA Security Lab試験の準備にあまり時間がかからないことを理解しています。したがって、異なるバージョンのS90.20試験トピック問題をあなたに提供します。読んで簡単に印刷するには、PDFバージョンを選択して、メモを取るのは簡単です。 もしあなたがSOA Security Labの真のテスト環境に慣れるには、ソフト(PCテストエンジン)バージョンが最適です。そして最後のバージョン、S90.20テストオンラインエンジンはどの電子機器でも使用でき、ほとんどの機能はソフトバージョンと同じです。SOA Security Lab試験勉強練習の3つのバージョンの柔軟性と機動性により、いつでもどこでも候補者が学習できます。私たちの候補者にとって選択は自由でそれは時間のロースを減少します。
現代IT業界の急速な発展、より多くの労働者、卒業生やIT専攻の他の人々は、昇進や高給などのチャンスを増やすために、プロのS90.20試験認定を受ける必要があります。 試験に合格させる高品質のSOA Security Lab試験模擬pdf版があなたにとって最良の選択です。私たちのSOA Security Labテストトピック試験では、あなたは簡単にS90.20試験に合格し、私たちのSOA Security Lab試験資料から多くのメリットを享受します。
SOA Security Lab 認定 S90.20 試験問題:
1.
A) Each record in Database A is classified as either private or public. After Service A is invoked by a service consumer (1), it authenticates the request message using an identity store and retrieves the corresponding authorization (2, 3). Once authorized, the service consumer's request is submitted to Database A (4), which then returns the requested data (5) If the service consumer has private access permissions, all of the returned data is included in Service A's response message (6). If the service consumer has public access permissions, then Service A first filters the data in order to remove all unauthorized private data records before sending to the response message to the service consumer (6).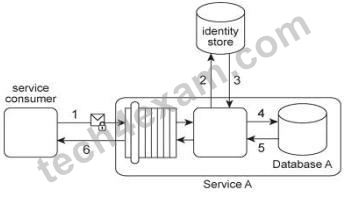
In addition to retrieving data, Service A's data access capability can be used to update database records. An investigation recently revealed an information leakage problem that can occur when service consumers with public access permissions attempt to update the ID value of a database record The ID values of all database records (private or public) must be unique. When a service consumer with public access permissions updates a public database record with an ID value that is already assigned to a private database record, the database returns an error message describing this conflict. This error text reveals confidential information by stating that the ID value submitted by the service consumer with public access permissions already exists within a private database record.
What steps can be taken to avoid this problem while preserving the requirement that all database records (private and public) have unique ID values?
B) The database rules are changed so that the ID value of database records no longer needs to be unique. As a further precaution, the Service A logic is changed to disallow the update of private database records by service consumers with only public access permissions.
C) When Service A detects that a service consumer with public access permissions has submitted an ID value that already exists within a private database record, it stores the service consumer's ID value in a temporary database and returns a response message indicating that the update was successful. A notification message is then sent to a human database administrator who manually contacts the owner of the service consumer in order to explain that the ID value submitted cannot be accepted because it already exists within a private database record.
D) The Exception Shielding pattern is applied to replace the error description text before a response message is returned to the service consumer. Furthermore, the ID value of all database records is appended with a code indicating whether the database record is private or public
E) The service consumer's request message containing the ID value can be encrypted by inserting the private key of the service consumer into the data. Because all service consumers have different private keys, this approach will lead to different encrypted values, even if the plain text ID values are the same. As a result, two data items with the same encrypted unique identifier cannot exist.
2. Service Consumer A sends a request message to Service A (1), after which Service A sends a request message to Service B (2). Service B forwards the message to have its contents calculated by Service C (3). After receiving the results of the calculations via a response message from Service C (4), Service B then requests additional data by sending a request message to Service D (5). Service D retrieves the necessary data from Database A (6), formats it into an XML document, and sends the response message containing the XML-formatted data to Service B (7).
Service B appends this XML document with the calculation results received from Service C, and then records the entire contents of the XML document into Database B (8). Finally, Service B sends a response message to Service A (9) and Service A sends a response message to Service Consumer A (10).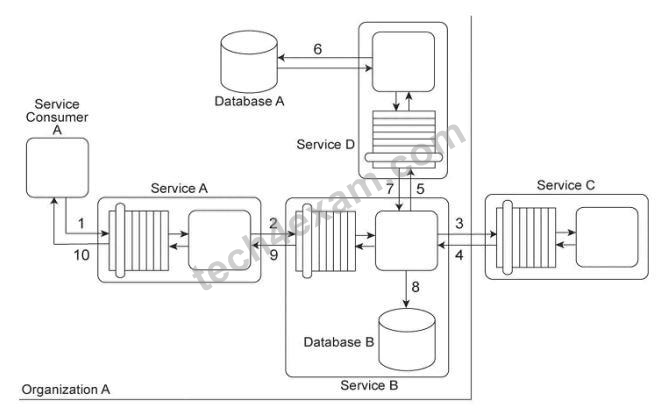
Services A, B and D are agnostic services that belong to Organization A and are also being reused in other service compositions. Service C is a publicly accessible calculation service that resides outside of the organizational boundary. Database A is a shared database used by other systems within Organization A and Database B is dedicated to exclusive access by Service B.
Service B has recently been experiencing a large increase in the volume of incoming request messages. It has been determined that most of these request messages were auto-generated and not legitimate. As a result, there is a strong suspicion that the request messages originated from an attacker attempting to carry out denial-of-service attacks on Service B.
Additionally, several of the response messages that have been sent to Service A from Service B contained URI references to external XML schemas that would need to be downloaded in order to parse the message data. It has been confirmed that these external URI references originated with data sent to Service B by Service C.
The XML parser currently being used by Service A is configured to download any required XML schemas by default. This configuration cannot be changed.
What steps can be taken to improve the service composition architecture in order to avoid future denial-of-service attacks against Service B and to further protect Service A from data access-oriented attacks?
A) Apply the Service Perimeter Guard pattern and the Message Screening pattern together to establish a service perimeter guard that can filter response messages from Service C before they reach Services A and B.
The filtering rules are based on the IP address of Service C.
If a request message originates from an IP address not listed as one of the IP addresses associated with Service C.
then the response message is rejected.
B) Apply the Service Perimeter Guard pattern to establish a perimeter service between Service B and Service C.
Apply the Brokered Authentication pattern by turning the perimeter service into an authentication broker that is capable of ensuring that only legitimate response messages are being sent to Service C from Service B Further apply the Data Origin Authentication pattern to enable the perimeter service to verify that messages that claim to have been sent by Service C actually originated from Service C.
Apply the Message Screening pattern to add logic to the perimeter service to also verify that URIs in request messages are validated against a list of permitted URIs from where XML schema downloads have been pre-approved.
C) Apply the Data Origin Authentication pattern so that Service B can verify that request messages that claim to have been sent by Service A actually did originate from Service A.
Apply the Message Screening pattern to add logic to Service A so that it can verify that external URIs in response messages from Service B refer to trusted sources.
D) Apply the Direct Authentication pattern so that Service C is required to provide security credentials, such as Username tokens, with any response messages it sends to Service B.
Furthermore, add logic to Service A so that it can validate security credentials passed to it via response messages from Service B.
by using an identity store that is shared by Services A and B.
3. Service A provides a customized report generating capability. Due to infrastructure limitations, the number of service consumers permitted to access Service A concurrently is strictly controlled. Service A validates request messages based on the supplied credentials (1). If the authentication of the request message is successful, Service A sends a message to Service B (2) to retrieve the required data from Database A (3). Service A stores the response from Service B (4) in memory and then issues a request message to Service C (5). Service C retrieves a different set of data from Database A (6) and sends the result back to Service A (7). Service A consolidates the data received from Services B and C and sends the generated report in the response message to its service consumer (8).
This service composition was recently shut down after it was discovered that Database A had been successfully attacked twice in a row. The first type of attack consisted of a series of coordinated request messages sent by the same malicious service consumer, with the intention of triggering a range of exception conditions within the database in order to generate various error messages. The second type of attack consisted of a service consumer sending request messages with malicious input with the intention of gaining control over the database server. This attack resulted in the deletion of database records and tables. An investigation revealed that both attacks were carried out by malicious service consumers that were authorized.
How can the service composition security architecture be improved to prevent these types of attacks?
A) Apply the Service Perimeter Guard pattern together with the Trusted Subsystem pattern.
This establishes a perimeter service between Database A and any service that requires access to it (including Services B and C). The perimeter service evaluates incoming data requests and filters out those that can introduce a security risk. Only request messages issued by authorized services and service consumers are forwarded to Database A.
Responses originating from Database A are further evaluated by the trusted subsystem to remove any unauthorized data. The two patterns together ensure that only authorized data is returned to the service consumer and that no request messages present a security threat to Database A.
B) Apply the Trusted Subsystem pattern to protect Database A from data-driven attacks and to evaluate whether database responses contain inappropriate data. The trusted subsystem maintains a snapshot of Database A and executes the original service consumer's request message against the snapshot. The processing logic that accesses the snapshot has limited privileges in order to prevent malicious attacks from overtaking the database. If no security violation is detected during the processing of the snapshot, then the original service consumer's request is forwarded to Database A.
If an error message is generated during the processing of the snapshot, then it is returned to the original service consumer and the request is not forwarded to Database A.
Because the error message was generated on the snapshot, it cannot contain unsafe information about Database A.
C) Apply the Data Confidentiality pattern together with the Data Origin Authentication pattern. This establishes message-level security so that all messages are encrypted and digitally signed. Secondly, the Service A logic must be enhanced so that it can keep track of the trustworthiness of its service consumers If a request message originated from a trustworthy service consumer, then the request message is processed as normal. If the request message originates from a non-trustworthy service consumer, then the request message is rejected and an error message is returned to the service consumer.
D) Apply the Exception Shielding pattern together with the Message Screening pattern.
This establishes new logic within Service A that screens incoming request messages for data-driven attacks (such as SQL injection and XPath injection attacks), and also evaluates whether exception details returned by Database A contains potentially confidential or unsafe information. Any inappropriate exception information is replaced with sanitized content.
質問と回答:
| 質問 # 1 正解: A、D | 質問 # 2 正解: C | 質問 # 3 正解: D |


 弊社は製品に自信を持っており、面倒な製品を提供していません。
弊社は製品に自信を持っており、面倒な製品を提供していません。



 原田**
原田**